 |
This is a good waveform |
 View larger image View larger image
 Download this waveform file for use with PicoScope Download this waveform file for use with PicoScope
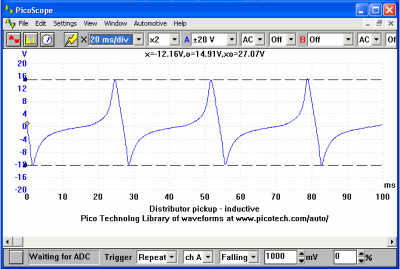
Distributor Inductive Pick-up (Engine Running) Waveform Notes
This particular type of pick-up generates its own signal and therefore does not require a voltage supply to power it. Recognisable by its two electrical connections, the pick-up is used as a signal to trigger the ignition amplifier or Electronic Control Module (ECM). As the metal rotor spins, a magnetic field is altered which induces an Alternating Current (AC) voltage from the pick-up. This type of pick-up could be described as a small alternator because the output voltage rises as the metal rotor approaches the winding, sharply dropping through zero volts as the two components are aligned and producing a voltage in the opposite phase as the rotor passes. The waveform is known as a sinewave.
The voltage produced by the pick-up will be determined by several factors, these being:
- Engine speed - the voltage produced will rise from as low as 2 to 3 volts when cranking to over 50 volts, at higher engine speeds.
- The proximity of the metal rotor to the pick-up winding. An average air gap will be in the order of 8 to 14 thou, a larger air gap will reduce the strength of the magnetic field seen by the winding and the output voltage will be subsequently reduced.
- The strength of the magnetic field offered by the magnet. The strength of this magnetic field determines the effect it has as it ‘cuts’ through the windings and the output voltage will be reduced accordingly.
A difference between the positive and the negative voltages may also be apparent as the negative side of the sinewave is sometimes attenuate when connected to the amplifier circuit, but will produce perfect AC when disconnected and tested under cranking conditions.
汽車(chē)診斷 | 汽車(chē)診斷儀 | 汽車(chē)故障診斷儀 | 汽車(chē)測(cè)試儀 | 汽車(chē)分析儀 | 汽車(chē)診斷示波器 | 汽車(chē)電路測(cè)試儀 | 汽車(chē)電路分析儀 | 發(fā)動(dòng)機(jī)分析儀 | 發(fā)動(dòng)機(jī)綜合分析儀 | 發(fā)動(dòng)機(jī)檢測(cè)中心 | 點(diǎn)火分析儀 | 點(diǎn)火測(cè)試儀 | 汽車(chē)傳感器測(cè)試儀 | CAN總線示波器 | LIN總線示波器 | 汽車(chē)故障記錄儀 | 汽車(chē)傳感器分析儀 | 汽車(chē)檢測(cè)儀 | 噴油嘴測(cè)試儀 | 點(diǎn)火線圈測(cè)試儀 | 蓄電池測(cè)試儀 | 發(fā)電機(jī)測(cè)試儀 | 起動(dòng)機(jī)測(cè)試儀 | ABS傳感器測(cè)試儀 | ECU測(cè)試儀 | ECM測(cè)試儀 | 進(jìn)氣真空/壓力測(cè)試儀 | 排氣壓力測(cè)試儀 | 汽車(chē)技術(shù)培訓(xùn) | 爆震傳感器測(cè)試儀 | 缺火測(cè)試儀 | 缺缸測(cè)試儀 | 線路測(cè)試儀 | 引出線 | 汽車(chē)數(shù)字示波器 | 真空傳感器 | 高壓感應(yīng)測(cè)試頭 | 無(wú)分電器點(diǎn)火測(cè)試頭 | 獨(dú)立點(diǎn)火(COP)感應(yīng)測(cè)試頭 | 漏電測(cè)試儀 | 氣缸相對(duì)壓縮測(cè)試 | 電腦測(cè)試儀 | 發(fā)動(dòng)機(jī)控制器測(cè)試儀 | 泄漏測(cè)試儀 | 熒光檢漏 | 超聲波檢漏 | 汽車(chē)數(shù)字萬(wàn)用表 | 電流鉗表 | 電流勾表 | 點(diǎn)火正時(shí)燈 |



